Briefing paper on ICD-11 and PVFS, ME and CFS: Part 1
September 29, 2014
Post #315 Shortlink: http://wp.me/pKrrB-40E
Part one of a three part report on the status of ICD-11 proposals for the classification of the three ICD-10 entities:
G93.3 Postviral fatigue syndrome (coded under parent class G93 in Tabular List)
Benign myalgic encephalomyelitis (inclusion term to G93.3 in Tabular List)
Chronic fatigue syndrome (indexed to G93.3 in Volume 3: Alphabetical Index)
Part 1: Status of the ICD-11 development process
Part 3: Status of proposals for the revision of ICD-10’s Somatoform disorders for the core and primary care versions of ICD-11
Part 1: Status of the ICD-11 development process
The revision of ICD-10 and development of the structure for ICD-11 began in April 2007.
ICD-11 was originally planned for completion by 2012, but the timeline was extended to 2015 early in the development process.
In January 2014, WHO/ICD Revision extended the timeline by a further two years to allow more time for generation of content, peer review, field testing and evaluation, translations and transition preparations [1].
The current projected date for approval by the World Health Assembly (WHA) is May 2017 with implementation timelined for 2018+.
In July 2014, WHO issued a call for expressions of interest in a contract for an external interim assessment of the revision process. Due date for the assessment report is December 15, 2014. It is not known whether WHO intends to publish a summary of the external assessment report.
Once ICD-11 is ready for dissemination, WHO Member States will transition to the new edition at their own pace. There is no WHO mandated date by which ICD-11 must be implemented, but WHO has said that it won’t support the annual updating of ICD-10 indefinitely. Developing and low resource countries may take many years before migrating to ICD-11.
Print and electronic versions
The scope of the revision project is ambitious and technically very complex. The project is under-resourced and underfunded and there is no overall project manager. Work groups have complained about the burden of work and poor internal communications.
There will be an ICD-11 print edition and a more expansive computerized version planned to be integrable with the international SNOMED CT terminology system.
The electronic version has a Foundation Component which includes all the ICD-11 diagnostic categories arranged in hierarchical “trees.”
From the Foundation Component, subsets (known as “linearizations”) are derived that contain mutually exclusive lists of terms for different purposes, e.g. for mortality, morbidity or primary care.
There are anticipated to be linearizations for mental and behavioural disorders, low resource and high resource primary care settings, rare diseases and occupational health and speciality classifications, including neurology, paediatrics, ophthalmology and dermatology.
The public version of the Beta drafting platform currently displays only the Foundation Component and a Joint Linearization for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics.
The country specific “Clinical Modifications” of ICD-10, including the U.S.’s forthcoming ICD-10-CM, are expected to be incorporated into ICD-11, as linearizations, as is ICPC-2.
The development process is overseen by a Revision Steering Group (RSG) chaired by biomedical informatics expert, Christopher Chute, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN [2].
Primary Care version
ICD-10 PHC (sometimes written as ICD-10-PHC or ICD10-PHC or ICD-10 PC), is a simplified version of the WHO’s ICD-10 chapter for mental and behavioural disorders for use in general practice and primary health care settings. This system has rough but not exact equivalence to mental disorders in the core ICD-10 classification.
The ICD-10 PHC describes 25 disorders commonly managed within primary care as opposed to circa 450 classified within Chapter V of ICD-10.
An revised version, known as ICD-11 PHC, is being developed simultaneously with the core version.
The ICD-11 Primary Care Consultation Group, chaired by Prof Sir David Goldberg, is charged with the revision of the 26 mental and behavioural disorders in ICD-10 PHC. The 28 mental disorders proposed for the new primary care edition (ICD-11 PHC) will require an equivalent category within the core ICD-11 version [5].
Work Groups
Over 20 work groups have been assembled since 2007 reporting to the RSG. These are known as Topic Advisory Groups (TAGs). Professional and scientific organisations also have representatives on the TAGs [3].
TAG Managing Editors may also recruit external reviewers for reviewing proposals and textual content. Terms of Reference for TAGs and work groups can be viewed in reference [4].
Reporting to the TAGs are sub working groups charged with making recommendations for specific chapter sections. TAG membership lists are available from the WHO site but the names of sub working group members and external reviewers are not posted.
The Work Groups with most relevance for the ICD-10 G93.3 categories are:
TAG Neurology (Diseases of the nervous system) Chair: Prof Raad Shakir, Managing editor: Tarun Dua, WHO.
TAG Mental Health (Mental and behavioural disorders) Co-Chairs: Geoffrey Reed, PhD, WHO; Steven Hyman, MD, Harvard University.
ICD-11 Expert Working Group on Somatic Distress and Dissociative Disorders (S3DWG) Chair: Prof Oye Gureje. A sub working group to TAG Mental Health. Prof emeritus, Francis Creed, is a member. This group is said to have 17 members but apart from two others, I have been unable to establish the full membership list.
ICD-11 Primary Care Consultation Group (PCCG) Chair: Prof Sir David Goldberg, Vice-chair: Prof Michael Klinkman (U.S.). Per Fink’s research collaborator, Marianne Rosendal, is a member of the 12 person, PCCG. The full member list has been published in a journal paper [5] but is not posted on the WHO website.
Differences between ICD-10 and ICD-11
There are significant differences between the structure of ICD-10 and ICD-11: more chapters (currently 26 against ICD-10’s 22); reordering of chapters; restructuring of disease classes and parent/child hierarchies within chapters; renaming of some terms; relocation of some terms to other existing chapters or to new chapters; multiple linearizations; more descriptive content; a new system of code numbers.
Disease terms with an equivalent ICD-10 term are back referenced to their legacy terms and codes in the electronic platform for ICD-10 Version: 2010 [6].
Multiple parents and multisystem diseases
For ICD-10 Tabular List, an ICD entity (a parent class, title term or inclusion term) can appear in only one place within the classification.
For ICD-11, multiple parentage is permissible. In the Foundation Component, disorder or disease terms can appear under more than one hierarchical parent [7].
Diseases that straddle two chapters, like malignant neoplasms of the skin, can now be viewed under Diseases of the skin as well as cross-linking to the Neoplasms chapter. Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD), proposed for inclusion in ICD-11, is listed under both Depressive disorders, in the Mental and behavioural disorders chapter, and also under Premenstrual tension syndrome under new chapter, Conditions related to sexual health.
So the ICD-10 concept of discrete chapter location is being dispensed with for ICD-11.
In 2010, the Revision Steering Group posted a discussion paper on the potential for incorporating a new chapter into ICD-11 for Multisystem diseases, but this proposal has been rejected [8].
In 2013, consideration was being given, instead, for generating a multisystem diseases linearization – as a virtual chapter – compiled from the Foundation Component that lists all ICD disorders and diseases, but there would be no separate Multisystem diseases chapter within the print version [9].
It isn’t known whether a decision has been reached but there is currently no ability to generate a multisystem diseases linearization from the Foundation Component, at least not within the public version of the Beta drafting platform.
How to represent multisystem diseases within ICD-11 (and the potential for an ICD category term to be assigned to multiple parents) could have implications for classification of one or more of the three ICD-10 G93.3 terms.
The Content Model
Another major difference between ICD-10 and ICD-11 is the Content Model. For ICD-11, all uniquely coded ICD Title terms (but not their Inclusion terms or Synonyms) are intended to have Definitions and in some cases, other descriptive content populated [10]. Whereas category terms located in ICD-10 chapters other than Chapter V: Mental and behavioural disorders were listed, to quote WHO’s, Bedirhan Üstün, like a laundry list, with no descriptive content.
Outside of the WHO classification experts, the RSG, the working groups, sub working groups and their external advisers who else is inputting into the development process?
In 2009, ICD Revision Steering Group began inviting professional bodies and Royal Colleges to submit proposals for revisions to the ICD structure and content for ICD-11.
WHO has also set up a Global Clinical Practice Network (GCPN), an international network of over 11,000 mental health and primary care professionals [11].
Calls have gone out for various classes of professional stakeholder to register with the public version of the Beta draft to participate in the revision process:
Medicine; Nursing; Midwifery; Dentistry; Pharmacy; Health information management (coding, medical records); Environmental and occupational health and hygiene; Physiotherapy or Physical therapy; Nutrition; Social Sciences; Psychology; Social work and counseling; Epidemiology; Health Policy; Traditional and complementary medicine.
A pre-final draft for ICD-11 is expected to be released for public comment at some point in 2015/16, but no firm date for this has been announced.
How can stakeholders participate?
Professional stakeholders and others who register an interest are able to interact with the Beta drafting platform and access additional content, e.g. PDFs of the print versions and Index.
The public version of the Beta drafting platform can be viewed without registration but comments submitted by registered stakeholders are not visible to non registered viewers.
Comments and suggestions are screened and forwarded to the appropriate TAG Managing editors for review. Occasionally, a TAG Managing editor or one of the ICD Revision staff will respond to a proposal or a request for correction via the comments facility.
Registered stakeholders are permitted to:
• Add comments on and read other stakeholder comments on concepts; title terms; synonyms; inclusion terms; exclusions and other Content Model parameter terms;
• Comment on whether a category is in the right place;
• Comment on whether the category is useful for Primary Care; Research; Clinical;
• Suggest definitions (with sources) for a disease or disorder and comment on already populated draft definitions;
• Make proposals to change ICD categories, supported with references;
• Offer to participate in field trials (for professionals only);
• Offer to assist in translating ICD into other languages
Stakeholders can register for participation here: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/revision/en/
Video inviting professional and stakeholder participation here: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/revision/video/en/
The Beta platform is intended for considered and collegiate input – not as a platform for campaigning or activism.
Some patient advocacy organisations, for example, gender and trans* groups, have been holding face to face meetings with ICD Revision personnel at conferences or other venues to inform the revision process and represent their constituencies’ interests.
A new Proposals mechanism was launched on the public Beta draft in July 2014. This is a more sophisticated system through which registered users can submit proposals, supported with rationales and references, for changes/additions/deletions to proposed ICD-11 entities.
Proposals guide: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/Help/Get/proposal_main/en
Where to view the Beta drafting platform
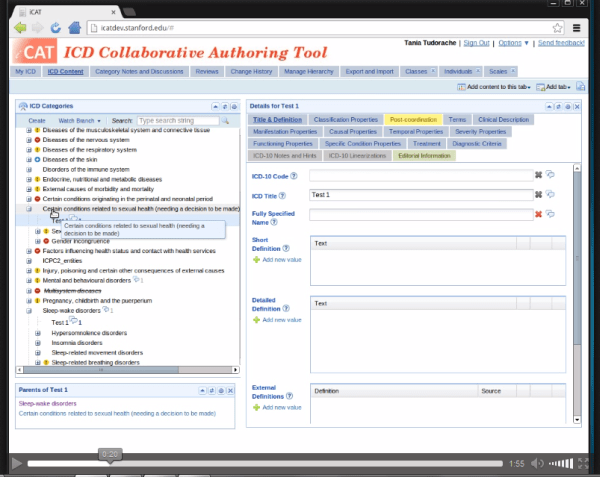
ICD Revision and TAG Managing editors are developing the Beta draft on a separate electronic multi-authoring platform, known as the iCAT, on a server which is not accessible to the public.
The iCAT Beta platform is more layered than the Beta version which the public sees: it displays a larger number of “Content Model” parameters; there are tabs for tracking “Change Histories” and “Category Notes and Discussions” for comparing earlier iterations of a specific chapter section with the most recent edits. There are sub lists for terms that are proposed to be retired or for which decisions are needing to be made.
The public version of the Beta has no means through which changes to the draft (and rationales for changes) can be tracked, or for comparing, for example, an earlier edit of a specific chapter section with the most recent content.
The inability to monitor editing histories in the public Beta draft and the absence of progress reports from the work groups adds to confusion around interpretation of the Beta content. The draft is updated daily, so it needs checking every day for relevant changes.
You can view the public version of the Beta drafting platform here:
http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/f/en
Foundation Component (the entire ICD universe):
http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/f/en#/
Joint Linearization for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics:
http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/l-m/en#/
User Guide: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/Help/en
Click on the small grey arrows next to the Beta draft categories to display their parent, child and grandchildren categories, as drop down hierarchies.
 Select this coloured button to display symbols and hover text indicating which linearization(s) a selected term is listed under.
Select this coloured button to display symbols and hover text indicating which linearization(s) a selected term is listed under.
The display panel on the right contains the “Content Model” text: Short and Long Definitions, Inclusion terms, Synonyms, Exclusions, Index terms etc. for the selected ICD Title term. Many terms are still awaiting population of Short Definitions (for print version) and Long Definitions (for electronic version), and other descriptive content.
For comparison between the public Beta draft and the iCAT, view this 2 minute iCAT screencast animation (with audio), intended as a demo for ICD Revision editors.
The animation is an .ogv file which should run in recent releases of Firefox but may not load in other browsers. If you don’t have the right program installed to run an .ogv file, the iCAT multi-authoring platform that the TAG editors are using looks like this:
In Part Two, I shall be setting out what is currently known about proposals for the classification of Postviral fatigue syndrome, Benign myalgic encephalomyelitis and Chronic fatigue syndrome for ICD-11.
Important caveats: The public Beta platform is not a static document, it is a work in progress, subject to daily editing and revision, to field test evaluation and to approval by the RSG and WHO classification experts. Not all new proposals may survive the ICD-11 field tests. Chapter numbering, codes and “sorting codes” currently assigned to ICD categories are not stable and will change as chapters and parent/child hierarchies are reorganized. The public version of the Beta is incomplete; not all “Content Model” parameters display or are populated; the draft may contain errors and omissions.
Part 2: Status of proposals for the classification of PVFS, BME, and CFS in the public version of the ICD-11 Beta drafting platform published September 30, 2014
Part 3: Status of proposals for the revision of ICD-10’s Somatoform disorders for the core and primary care versions of ICD-11 [to follow]
References for Part 1
1 Committee for the Coordination of Statistical Activities, Twenty-second Session 4-6 September 2013, Items for discussion and decision: Item 8, provisional agenda, pp 8-10: http://unstats.un.org/unsd/accsub/2013docs-22nd/SA-2013-12-Add1-Health-WHO.pdf
2 http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/RSG/en/
3 http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/TAGs/en/
4 http://www.who.int/entity/classifications/TOR_TAGs_WGs.pdf?ua=1
5 Lam TP, Goldberg DP, Dowell AC, Fortes S, Mbatia JK, Minhas FA, Klinkman MS: Proposed new diagnoses of anxious depression and bodily stress syndrome in ICD-11-PHC: an international focus group study. Family Practice (2012) 30 (1): 76-87. Free text: http://fampra.oxfordjournals.org/content/30/1/76.full.pdf+html
6 http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/f/en#/
7 http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd11/browse/Help/Get/architecture/en
10 http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/revision/contentmodel/en/
