WHO approves exclusions for PVFS, ME and CFS under ICD-11’s Bodily distress disorder
February 19, 2020
Post #356 Shortlink: https://wp.me/pKrrB-555
An edited version of this report is scheduled for publication in the March edition of the ME Global Chronicle.
For ICD-11, most of the ICD-10 F45 Somatoform disorders categories and F48.0 Neurasthenia have been replaced by a single new category called “Bodily distress disorder” (BDD).
Although this sounds like it might be very similar to Per Fink’s Bodily distress syndrome (BDS), ICD-11’s BDD is conceptually closely aligned with the DSM-5’s Somatic symptom disorder (SSD).
For ICD-11, Somatic symptom disorder is listed under Synonyms under BDD but is not coded as an inclusion term.
Both the WHO and Prof Fink have clarified that as defined for ICD-11, BDD is a conceptually different disorder construct — ICD-11’s BDD and Fink’s BDS are differently defined and characterised, have very different criteria and are inclusive of different patient sets.
For ICD-11, the BDD diagnosis requires both the presence of one or more chronic, distressing bodily symptoms (which can be “medically unexplained” or caused or exacerbated by a general medical condition) and “excessive attention” or “disproportionate or maladaptive” thoughts, feelings or behavioural responses to these symptoms. BDD can capture a percentage of patients with ME, CFS or other general medical diseases or conditions — if the clinician considers the patient also meets the disorder description for application of an additional mental disorder diagnosis of BDD.
In contrast, Fink’s BDS disorder construct requires physical “symptom patterns” or “clusters” from one or more body systems; the symptoms must be “medically unexplained” and there is no requirement for emotional or behavioural responses to meet the criteria. If the symptoms can be better explained by a general medical disease, they cannot be labelled “BDS”. But crucially, Fink’s BDS is inclusive of ME, CFS, IBS and FM and subsumes these under a single, unifying diagnosis.
The terms “bodily distress disorder” and “bodily distress syndrome” have been used synonymously since 2007. Not surprisingly, researchers, academics and practitioners are already confusing and conflating ICD-11’s new “Bodily distress disorder” with Fink’s “Bodily distress syndrome”.
Although BDD can potentially be applied to patients with chronic, distressing symptoms associated with any general medical disease or condition, patients with a diagnosis of ME or CFS (or who are waiting for a diagnosis) may be particularly vulnerable to misdiagnosis with BDD or misapplication of an additional BDD mental disorder diagnosis, as a “bolt-on” to their existing diagnosis.
Exclusions for the 8E49 terms under MG22 Fatigue and a reciprocal exclusion for MG22 Fatigue under 8E49 Postviral fatigue syndrome were secured by April 2019.
However, the need for adding exclusions for PVFS, ME and CFS under ICD-11’s BDD to mitigate the risk of misdiagnosis or misapplication had not been acknowledged or accepted by the WHO.
In my report in the December edition of the ME Global Chronicle, I mentioned that the proposals submitted by Chapman & Dimmock (March 2017) and by Lily Chu MD on behalf of IACFS/ME (March 2017) for exclusions for the three 8E49 terms under 6C20 Bodily distress disorder and for exclusion of 6C20 Bodily distress disorder under the 8E49 Postviral fatigue syndrome concept title had been rejected.
In December 2019, I submitted a new proposal for exclusions for the three 8E49 terms under 6C20 Bodily distress disorder, supported by a new rationale text.
I am very pleased to inform you that in January the WHO approved and implemented my proposal.
You can view the addition of the three exclusions under ICD-11’s Bodily distress disorder here: https://icd.who.int/dev11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/767044268
Image 1: ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics (Maintenance Platform), Accessed February 18, 2019:
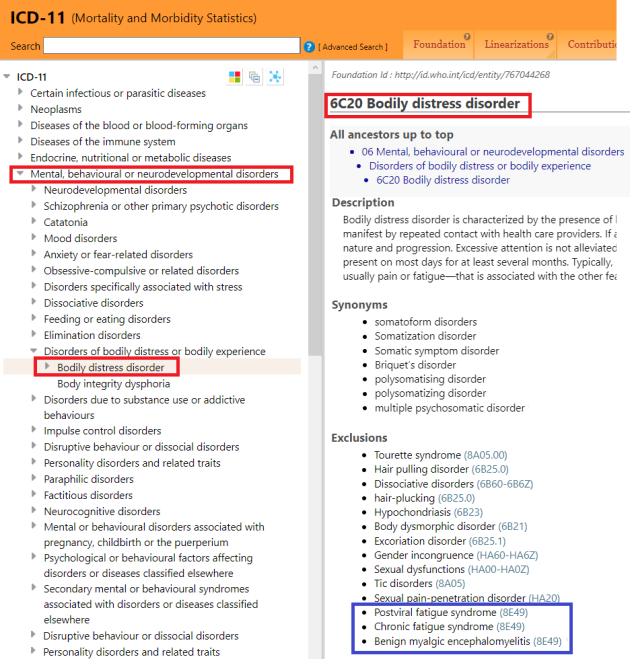
I have updated the PDF of my report in the December edition to reflect the addition of exclusions.
Download my updated report here: http://bit.ly/ICD11Update
The WHO Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines (CDDG) for ICD‐11 Mental, Behavioural and Neurodevelopmental Disorders:
For ICD-11, the WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse has developed the “Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines (CDDG) for ICD‐11 Mental, Behavioural and Neurodevelopmental Disorders” (an equivalent publication to ICD-10’s “Blue Book”).
The CDDG provides expanded clinical descriptions, essential (required) features, boundaries with other disorders and normality, differential diagnoses, additional features, culture-related features and codes for all mental and behavioural disorders commonly encountered in clinical psychiatry. This companion publication is intended for mental health professionals and for general clinical, educational and service use.
The WHO has said it planned to release the CDDG “as soon as possible” after WHA’s adoption of ICD-11. But it remains unclear whether the CDDG has been finalised or if it will be released later this year or next year.
See this post Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines (CDDG) for ICD‐11 Mental, Behavioural and Neurodevelopmental Disorders for more information.
Whilst clinicians have been able to register to review and provide feedback on the drafts, no draft texts for the CDDG have been made available for public stakeholder scrutiny and comment and I have not had access, for example, to the most recent draft for the full clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines for ICD-11’s Bodily distress disorder.
Additional resources:
Comparison of SSD, BDD, BDS, BSS in classification systems, Chapman & Dimmock, July 2018
Comparison of Classification and Terminology Systems, Chapman & Dimmock, July 2018
Post: World Health Assembly adopts ICD-11: When will member states start using the new edition? June 17, 2019
Post: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines (CDDG) for ICD‐11 Mental, Behavioural and Neurodevelopmental Disorders, June 28, 2019
