ICD-11 December Round up #1
December 13, 2013
Post #286 Shortlink: http://wp.me/pKrrB-3AJ
“The current ICD Revision Process timeline foresees that the ICD is submitted to the WHA in 2015 May and could then be implemented…experience obtained thus far, however, suggests that this timeframe will be extremely tight for paying due diligence to the work especially in terms of: appropriate consultations with expert groups; communication and dissemination with stakeholders; and sufficient time for field testing in multiple countries and settings, and carrying out the resulting edits.” B Üstün, September 2013
In this September posting, I reported that a further extension to the ICD-11 timeline is under consideration.
This document and this slide presentation (Slides 29 thru 35) indicate that ICD-11 Revision is failing to meet development targets.
In a review of progress made, current status and timelines (document Pages 5 thru 10), Dr Bedirhan Üstün, Coordinator, Classification, Terminology and Standards, World Health Organization, sets out the options for postponement and discusses whether submission of ICD-11 for World Health Assembly approval should be delayed until 2016, or possibly 2017.
I will update as further information on any decision to extend the timeline emerges.
Round up of ICD-11 related materials:
Slide presentation: PDF format, mostly in German
58. GMDS-Jahrestagung, Lübeck, 1.-5.9.2013: Symposium, Medizinische, Klassificationen und Termiologien Vortrag Üstün und Jakob, 5.9.2013
ICD-11 Übersicht Üstün und Jakob
Slide presentation: Slideshare format, in English
Regional Conference of the International Society for Adolescent Psychiatry and Psychology (ISAPP)
Diagnostic Classifications in the 21st Century: how can we capture developmental details Bedirhan Üstün, Coordinator, World Health Organization, November 24, 2013
Multisystem diseases and terms with multiple parents:
In 2010, ICD-11 Revision posted this Discussion Document: Multisystem Disorders, Aymé, Chalmers, Chute, Jakob.
The text sets out the feasibility, rationale for and possible scope of a new multisystem disorders chapter for ICD-11 for diseases that might belong to or affect multiple body systems.
A more recent working document (WHO ICD Revision Information Note, R Chalmers, MS docx editing format, dated 29 January 2013) updates the discussion and concludes that a majority of ICD Revision Topic Advisory Groups and experts did not agree with the recommendation to create a new Multisystem Disease Chapter for ICD-11 and that other options for accommodating diseases which straddle multiple chapters were being considered.
According to ICD-11 Beta drafting platform, the ICD-11 Foundation Component will allow for a single concept to be represented in a Multisystem Disease linearization and appear in more than one logically appropriate location. In the linearizations (e.g. Morbidity), a single concept has a single preferred location and references [to the term] from elsewhere [within the same chapter or within a different chapter] are greyed out but link to the preferred location.
For example, skin tumour is both a skin disease and a neoplasm and for ICD-11 is located under two chapters. Other diseases that are proposed to be assigned multiple parents include some eye diseases resulting from diabetes; tuberculosis meningitis (as both an infectious and a nervous system disease) and Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), currently proposed to be dual coded under Chapter 15 Diseases of the genitourinary system under parent term, Premenstrual tension syndrome but also listed under Chapter 5 Mental and behavioural disorders under Depressive disorders.
While previous versions of ICD did not support multiple inheritance, there are already over 450 terms with multiple parents within ICD-11.
Editorial commentary, ICD-11 Neurological disorders:
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry doi:10.1136/jnnp-2013-307093
The classification of neurological disorders in the 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)
Sanjeev Rajakulendran¹, Tarun Dua², Melissa Harper², Raad Shakir¹
1 Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust, Charing Cross Hospital, London, UK; 2 Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Published Online First 18 November 2013 [Full text behind paywall]
Abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24249782
Single page extract as image: http://jnnp.bmj.com/content/early/2013/11/18/jnnp-2013-307093.extract
(If a single page text file fails to load at the above link, try pasting the editorial title into a search engine and access the page from the search engine link.)
Primary Care version of ICD-11 (ICD-11-PHC):
The ICD-10-PHC is an abridged version of the ICD-10 core classification for use in primary care and low resource settings. A new edition (ICD-11-PHC) is being developed simultaneously with the core ICD-11.
For all new and revised disorders included in the ICD-11 Primary Care version there will need to be an equivalent disorder in the ICD-11 core classification.
The Mental and behavioural disorders section of ICD-11-PHC is expected to list 28 mental and behavioural disorders most commonly managed within primary care settings, as opposed to over 400 disorders in Chapter 5 of the core version.
The following ICD-10-PHC disorders are proposed to be dropped for ICD-11-PHC:
F40 Phobic disorders; F42.2 Mixed anxiety and depression; F43 Adjustment disorder;
F45 Unexplained somatic symptoms; F48 Neurasthenia; Z63 Bereavement, Source [4].
A list of the 28 proposed disorders for ICD-11-PHC, as they stood in 2012*, can be found on Page 51 of Source [5].
*This list may have undergone revision since the source published.
A new disorder term “Anxious depression” is proposed to be field tested for inclusion in ICD-11-PHC and is discussed in this recent paper by Prof, Sir David Goldberg, who chairs the Primary Care Consultation Group (PCCG) charged with the development of the primary care classification of mental and behavioural disorders for ICD-11:
Abstract: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/da.22206/abstract
Depression and Anxiety
DOI: 10.1002/da.22206
Review ANXIOUS FORMS OF DEPRESSION
David P. Goldberg
Article first published online: 27 NOV 2013 [Full text behind paywall]
There are further commentaries on the proposed new diagnoses of “anxious depression” and “bodily stress syndrome” in this 2012 paper:
Lam TP, Goldberg DP, Dowell AC, Fortes S, Mbatia JK, Minhas FA, Klinkman MS: Proposed new diagnoses of anxious depression and bodily stress syndrome in ICD-11-PHC: an international focus group study. Fam Pract 2012 Jul 28. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22843638 [Full text behind paywall]
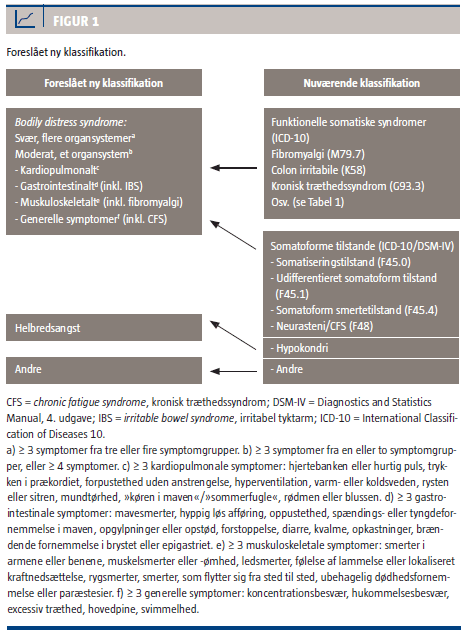
According to this earlier paper, the Primary Care Consultation Group (PCCG) was still refining a construct and criteria for its proposed new disorder category, which the group had tentatively named as “Bodily stress syndrome” (BSS).
BSS would replace ICD-10-PHC’s Unexplained somatic symptoms and Neurasthenia categories and would be located under a new disorder group section heading called “Body distress disorders,” under which would sit three other discrete disorders. See Page 51 of Source [5].
The characteristics of new disorder 15: Bodily stress syndrome (as they appeared in the paper) might be described as a mash-up between selected of the psychobehavioural characteristics that define DSM-5’s new Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) and selected of the characteristics and criteria for Fink et al’s Bodily Distress Syndrome – rather than a mirror or near mirror of one or the other.
In order to facilitate harmonization between ICD-11 and DSM-5 mental and behavioural disorders, we might envisage pressure on the group to align with or accommodate DSM-5’s new Somatic symptom disorder within any framework proposed to replace the existing ICD Somatoform disorders.
But DSM-5’s SSD and Fink et al’s BDS are acknowledged by Creed, Henningsen and Fink as divergent constructs, so this presents the groups advising ICD Revision with a dilemma if they are also being influenced to recommend a BDS-like construct.
You can compare how these two constructs differ and appreciate why it may be proving difficult to convince ICD Revision of the utility of the PCCG’s BSS construct (and the potential for confusion where different constructs bear very similar names) in my table at the end of Page 1 of this Dx Revision Watch post:
BDS, BDDs, BSS, BDD and ICD-11, unscrambled
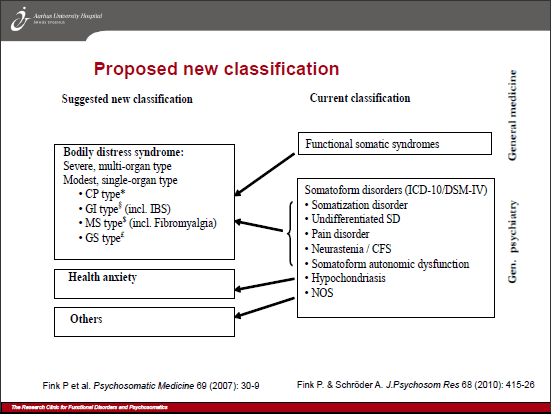
Marianne Rosendal (member of the ICD-11 Primary Care Consultation Group; member of WONCA International Classification Committee), Fink and colleagues are eager to see their Bodily distress syndrome construct adopted by primary care clinicians and incorporated into management guidelines and revisions of European classification systems to replace ICD-10’s F45 somatoform disorders, pain disorder, neurasthenia (ICD-10 F48), and the so-called “functional somatic syndromes,” Fibromyalgia (ICD-10 M79.7), IBS (ICD-10 K58) and CFS (indexed to ICD-10 G93.3). See graphics at end of post.
While Fink et al’s BDS construct seeks to capture somatoform disorders, pain disorder, neurasthenia and the so-called functional somatic syndromes under a single, unifying diagnosis, it is unclear from the 2012 Lam et al paper whether and how the so-called functional somatic syndromes are intended to fit into the Primary Care Consultation Group’s proposed ICD-11 framework.
While the paper does list some exclusions and differential diagnoses, it lists no specific exclusions or differential diagnoses for FM, IBS or CFS and it is silent on the matter of which of the so-called functional somatic syndromes the group’s proposed new BSS diagnosis might be intended to be inclusive of, or might intentionally or unintentionally capture.
Nor is it discussed within the paper what the implications would be for the future classification and chapter location of several currently discretely coded ICD-10 entities, if Bodily stress syndrome (or whatever new term might eventually be agreed upon) were intended to capture all or selected of FM, IBS, CFS and (B)ME – the sensitivities associated with any such proposal would not be lost on Prof Goldberg which possibly accounts for the lacunae in this paper.
Lack of consensus between the two groups advising ICD-11:
The second working group advising ICD-11 on the revision of ICD-10’s Somatoform disorders is the WHO Expert Working Group on Somatic Distress and Dissociative Disorders (S3DWG).
In late 2012, their emerging construct (also published behind a paywall) had considerably more in common with DSM-5’s SSD construct than with Fink et al’s BDS (see: BDS, BDDs, BSS, BDD and ICD-11, unscrambled).
But the S3DWG’s construct Bodily distress disorder (BDD) and Severe bodily distress disorder are yet to be defined and characterised in the public version of the ICD-11 Beta draft.
It remains unknown whether the two groups making recommendations for the revision of ICD-10’s Somatoform disorders have reached consensus over what definition and criteria WHO intends to field trial over the next year or two and what this proposed new diagnosis should be called; whether their proposed BDD/BSS/WHATEVER construct will have greater congruency with DSM-5’s SSD or with Fink et al’s BDS, or what patient populations this new ICD construct is intended to include and exclude.
The absence of information on proposals within the Beta draft, itself, and the lack of working group progress reports placed in the public domain presents considerable barriers for stakeholder comment on the intentions of these two groups and renders threadbare ICD-11’s claims to be an “open” and “transparent” and “inclusive” collaborative process.
Two further papers relating to “Medically unexplained symptoms,” “Bodily distress syndrome” and “Somatoform disorders”:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0163834313002533
General Hospital Psychiatry
Psychiatric–Medical Comorbidity
Is physical disease missed in patients with medically unexplained symptoms? A long-term follow-up of 120 patients diagnosed with bodily distress syndrome
Elisabeth Lundsgaard Skovenborg, B.Sc., Andreas Schröder, M.D., Ph.D.
The Research Clinic for Functional Disorders and Psychosomatics, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
Available online 22 October 2013 In Press, Corrected Proof [Full text behind paywall]
http://www.systematicreviewsjournal.com/content/2/1/99
Systematic Reviews 2013, 2:99 doi:10.1186/2046-4053-2-99
Barriers to the diagnosis of somatoform disorders in primary care: protocol for a systematic review of the current status
Alexandra M Murray¹²*, Anne Toussaint¹², Astrid Althaus¹² and Bernd Löwe¹²
1 Department of Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
2 University Hospital of Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy, Schön Clinic Hamburg-Eilbek, Hamburg, Germany
Published: 8 November 2013
[Open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License]
Finally, brief summaries of selected of the workshops held at the European Association for Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry and Psychosomatics (EACLPP) 2012 Conference, including workshops on “functional disorders and syndromes” and “Bodily distress,” one of which included:
http://www.eaclpp-ecpr2012.dk/Home/DownloadWorkshop
“…brief presentations which describe the present state of the proposed changes to Primary care classifications (ICPC and ICD for primary care) (MR) and DSM-V and ICD-11 (FC).”
where presenter “MR” is Marianne Rosendal; “FC” is Francis Creed, member of the ICD-11 Expert Working Group on Somatic Distress and Dissociative Disorders (S3DWG).
Note: ICPC-2 used in primary care is also under revision.
Foreslået ny klassifikation (Suggested new classification, Fink et al):
Source Figur 1: http://www.ugeskriftet.dk/LF/UFL/2010/24/pdf/VP02100057.pdf
References
1. WHO considers further extension to ICD-11 development timeline
2. Committee for the Coordination of Statistical Activities, Twenty-second Session 4-6 September 2013, Items for discussion and decision: Item 8 of the provisional agenda, 3 September 2013 Full document in PDF format
3. Slide presentation: ICD Revision: Where are we? What remains to be done? Shall we have ICD WHA submission in 2015 or later? Bedirhan Ustun, World Health Organization Classifications, Terminologies, Standards, ICD Revision: Quality Safety Meeting 2013, September 9-10, 2013 http://www.slideshare.net/ustunb/icd-2013-qs-tag-26027668
4. Goldberg, D. Guest editorial. A revised mental health classification for use in general medical settings: the ICD11–PHC 1. International Psychiatry, Page 1, February 2011. http://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/pdf/IPv8n1.pdf
5. Goldberg DP. Comparison Between ICD and DSM Diagnostic Systems for Mental Disorders. In: Sorel E, (Ed.) 21st Century Global Mental Health. Jones & Bartlett Learning, 2012: 37-53. Free PDF, Sample Chapter Two: http://samples.jbpub.com/9781449627874/Chapter2.pdf
 2013 All rights reserved. Current Biology,
2013 All rights reserved. Current Biology, 
Objectors to insertion of DSM-5’s Somatic symptom disorder into ICD-10-CM
November 16, 2013 by admindxrw
Post #283 Shortlink: http://wp.me/pKrrB-3y8
Michael Munoz, Executive Director, Rocky Mountain CFS/ME & FM Association has organized a joint letter of objection signed by 13 U.S. patient organizations and advocates for submission to NCHS. It can be read here:
http://www.rmcfa.org/index.html > http://www.rm-cfs-fms.citymaker.com/f/NCHS.pdf
or download PDF here: Joint response to NCHS 11.15.13
This joint submission had been signed by the following organizations and advocates:
I’d like to thank all those who have submitted objections to NCHS in opposition to the September 2013 C & M Committee meeting proposal to insert Somatic symptom disorder as an inclusion term in ICD-10-CM.
My submission can be read here PDF: Submission NCHS
Some additional organizations and individuals have advised me of their own submissions. If you have submitted a response on behalf of your organization or as a patient, advocate or professional and you would like your name or your organization’s name added to the list of responders below please shoot me an email or contact me via the Contact form with a link to your submission (if it has been placed in the public domain) and a couple of lines of credentials or stakeholder interest, if desired.
Share this:
Filed under American Psychiatric Association (APA), Darrel Regier, DSM-5, Functional Somatic Syndrome (FSS), ICD-10-CM, ICD-11, MUS, Myalgic encephalomyelitis, Somatic Symptom Disorder, Somatoform Disorders Tagged with american psychiatric association, dsm-5, functional somatic syndrome, icd-10-cm, icd-11, institute of psychiatry, NCHS, public comment, somatic symptom disorder, somatoform disorders