June 16, 2014
by admindxrw
You have until Friday in which to submit comments on any of the numerous diagnosis proposals presented at the March ICD-10-CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee meeting.
Comments should be sent to NCHS, preferably by email, by June 20th deadline: nchsicd9CM@cdc.gov
+++
The next public meeting of the ICD-10-CM/PCS Coordination and Maintenance Committee is scheduled for September 23–24, 2014. If you are planning to attend the meeting in person you will need to register online by September 12. Registration opens on August 15.
New proposals for the September 23–24, 2014 meeting must be received by July 18.
+++
September 2013 meeting Diagnosis Agenda
The fall meeting of the ICD-9-CM/PCS Coordination and Maintenance Committee took place on September 18–19.
The Diagnosis Agenda had included the proposals to add the new DSM-5 disorder terms: Somatic symptom disorder and Illness anxiety disorder to the ICD-10-CM Tabular List and the Alphabetical Index.
Note that the proposal was to add the terms as Inclusion Terms under existing ICD-10-CM Chapter 5 codes, not to create unique new codes for these two terms, or to replace or subsume any existing categories:

Source: Page 45, Diagnosis Agenda (Topic Packet), September 18–19, 2013 ICD-10-CM/PCS Coordination and Maintenance Committee Meeting
+++
March 2014 meeting Diagnosis Agenda
The spring C & M Committee meeting took place on March 19–20, 2014. I was unable to attend either meeting as I live in the UK, and it is not feasible for me to participate in these public meetings via phone link.
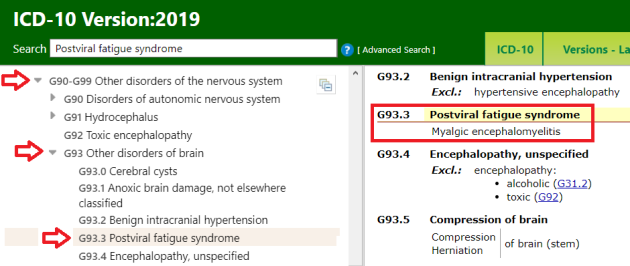
The March Diagnosis Agenda included reiteration of the September proposal to add Somatic symptom disorder to the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index, coded to F45.1. (But did not include a resubmission to add to the Tabular List.) The reason for its reiteration in the March Agenda is unclear.
When the March Agenda requests for additions and modifications to the Tabular List were reached, CDC’s Beth Fisher had remarked that some of the proposals for additions to the Tabular List may have been proposed at the September 2013 meeting (though no explanation was given for why some of these September proposals were being duplicated in the March Agenda).
Evidently some Index proposals from the September meeting were also duplicated in the March Agenda, including SSD, but not Illness anxiety disorder.
There were no comments or queries from the floor in relation to proposals for SSD. There were no queries about whether NCHS decisions had already been reached on the requests for additions and modifications submitted via the September meeting.
It remains unclear whether the duplications in the March Agenda were due to administrative oversight, were being included for procedural reasons, or were being re-presented in response to NCHS committee decisions made following the September meeting, to which APA, but not the public at large, might be party to. (The outcome of both the September and March proposals may not be evident until 2015, when the next Addendum is posted.)
March Agenda proposal: Add Somatic symptom disorder to the Index as “– somatic symptom F45.1” under “Disorders”:
+++

Source: Diagnosis Agenda (Topic Packet) Page 89, March 19-20, 2014 ICD-10-CM/PCS Coordination and Maintenance Committee Meeting; Screenshot Videocast Three
+++
F45.1 (SSD) and F45.21 (Illness anxiety disorder) are the ICD-10-CM codes to which these two new APA disorders are already cross-walked in the DSM-5:
+++

+++
If NCHS rubber stamps the addition of Somatic Symptom Disorder to the ICD-10-CM it could leverage future proposals (either by NCHS/CMS or by external requestors) for the replacement of some or all of the existing Somatoform disorders categories with this new, single SSD diagnostic construct, in order to bring ICD-10-CM in line with DSM-5.
There are implications for ICD-11, too. Once SSD is inserted into ICD-10-CM, the presence of this term within the U.S. adaptation of ICD-10 may make it easier for the ICD-11 Revision Steering Group to justify proposals to replace the existing ICD-10 Somatoform disorders categories with a single, new ICD construct incorporating SSD-like characteristics, to facilitate harmonization between ICD-11 and DSM-5 disorder terms and diagnostic criteria.
Comments by June 20th deadline, preferably by email, to: nchsicd9CM@cdc.gov
Below is my own submission to NCHS in PDF
 NCHS Submission Chapman June 14
NCHS Submission Chapman June 14
and as text:
To: NCHS nchsicd9CM@cdc.gov
Re: Comment on proposals, March 19-20, 2014 meeting of ICD-10-CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee.
Diagnosis Agenda Page 89: Under “Proposed Index Modifications”: Add Somatic symptom disorder to ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index (F45.1)
Proposal requestor: Unspecified
Comment submitted by Suzy Chapman DipAD, [Address redacted]
Date submitted: June 15, 2014
I write in objection to the proposed addition of Somatic symptom disorder to the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index for consideration for implementation on October 1, 2015 [or on and after October 1, 2016 after the partial code freeze has ended, as applicable].
This March 19-20, 2014 meeting proposal duplicates the request at the September 18-19, 2013 meeting for the addition of Somatic symptom disorder to the ICD-10-CM Index (and to the Tabular List) as an Inclusion Term to existing code, F45.1 Undifferentiated somatoform disorder.
Somatic symptom disorder is a new disorder conceptualization created by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for DSM-5.
For DSM-5, the Somatoform Disorders have been dismantled. Four DSM-IV categories: somatization disorder [300.81], some presentations of hypochondriasis [300.7], pain disorder, and undifferentiated somatoform disorder [300.82] are eliminated and replaced with a single new diagnosis, Somatic symptom disorder (SSD), cross-walked in DSM-5 to ICD-9 300.82 (ICD-10-CM F45.1).
The Somatic symptom disorder construct de-emphasizes “medically unexplained” as the central defining feature of this disorder group. Instead, the focus shifts away from somatic symptoms to emotional, cognitive and behavioral disturbances and “maladaptive” responses to symptoms: high levels of health anxiety; disproportionate and persistent concerns about the medical seriousness of the symptom(s); or an excessive amount of time and energy devoted to symptoms and health concerns.
Symptoms may or may not be associated with another medical condition: SSD allows for the application of a mental disorder diagnosis in patients with “established general medical conditions or disorders” like diabetes, heart disease and cancer or presenting with “somatic symptoms of unclear etiology” if the clinician considers the patient otherwise meets the new criteria.
To meet the requirements for DSM-IV’s Somatization disorder, a rigorous criteria set needed to be fulfilled: a history of many medically unexplained symptoms before the age of thirty, resulting in treatment sought or psychosocial impairment. And a high diagnostic threshold: a total of eight or more medically unexplained symptoms from four, specified symptom groups, with at least four pain, two gastrointestinal, one psychosexual and one pseudoneurological symptom.
In DSM-5, the requirement for eight symptoms has been dropped to just one or more persistent, non specific, distressing somatic symptoms and the clinician’s perception of “excessive” or “maladaptive” response to the symptom or symptoms.
• These changes for DSM-5 represent a radical restructuring of the DSM-IV Somatoform disorders framework and introduce a new construct for which much remains to be determined.
On Day Two of the September 18-19, 2013 ICD-9-CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee meeting, Dr Darrel Regier had presented and discussed rationales, coding proposals and timings for six new DSM-5 disorders that APA has proposed for insertion into ICD-10-CM. But the Diagnosis Agenda proposals to add the new DSM-5 Somatic symptom disorder and Illness anxiety disorder category terms as inclusion terms to ICD-10-CM did not form part of Dr Regier’s presentation.
As it was unspecified within the Diagnosis Agenda and during the meeting presentations, it is unclear whether these two proposals are being requested by APA, by NCHS/CMS, or by other parties or individuals.
+++
• My first concern is that no description of Somatic symptom disorder, no rationale for why this ICD-10-CM modification is needed (including clinical relevancy) and no supporting clinical and literature references for the validity of Somatic symptom disorder as a new disorder were published in the Diagnosis Agenda for either the September or March meeting.
At the public meeting, no presentation had been made on behalf of APA, or by representatives of NCHS or CMS, or by anyone else for the specific Agenda proposal to add Somatic symptom disorder as an inclusion term under an existing ICD-10-CM Somatoform disorders code and there was no discussion of this proposal during the course of the meeting [1][2].
There is an expectation that the committees overseeing the development and revision of the draft for ICD-10-CM will give due consideration to the applicability, clinical utility, safety and reliability of any proposal for the inclusion of a new disorder construct before granting approval for its addition to the Tabular List and Index, and that the comments and objections received during the public response period will also be considered. The lack of rationales and references for supportive evidence provided by the requestors hinders public participation in the response process.
• The absence from the Diagnosis Agendas and meeting presentations of rationales, clinical relevancy and supporting clinical and literature references to enable proper public scrutiny, consideration and informed responses to this proposal should disqualify Somatic symptom disorder from consideration for implementation once the partial code freeze has lifted.
+++
The burden of proof before introducing any new diagnosis into a classification system is that it has a favourable risk to benefit ratio. This new diagnostic construct created by APA and introduced into DSM-5 merits the same level of scrutiny and risk to benefit evaluation as would be expected to be applied to any proposed new disorder/disease that is under consideration for inclusion in any chapter of ICD, whether this is for the updating of the ICD-10-CM draft, updating of WHO’s ICD-10, updating of clinical modifications of ICD-10, or drafting of ICD-11.
A number of papers have noted the paucity of rigorous evidence for the validity, reliability, acceptability, safety and utility of the application of the Somatic symptom disorder construct in adults and children across diverse clinical settings and by a spectrum of health and allied professionals. There is no significant body of published research on the epidemiology, clinical characteristics or treatment of the Somatic symptom disorder construct [3][4][5].
In a paper published in the Journal of Psychosomatic Research, September 2013, the DSM-5 Somatic symptom disorder Work Group concedes the lack of clinical evidence for its new construct and acknowledges the “small amount of validity data concerning SSD” and “that much remains to be determined” about the utility and reliability of the specific SSD criteria and its thresholds when applied in busy, general clinical practice, and there are “vital questions that must be answered” as they go forward [6].
• As an under researched, poorly validated disorder construct, Somatic symptom disorder does not meet NCHS/CMS criteria for new diseases/new technology procedures, and any minor revisions to correct reported errors in these classification and should be rejected for consideration for implementation during a partial code freeze and also rejected for consideration for implementation on or after October 1, 2015 [October 1, 2016].
+++
Concerns for the looseness of the Somatic symptom disorder definition and the ease with which these new criteria can be met have been discussed in a number of published papers and commentaries [7][8][9][10].
The over-inclusiveness of the SSD diagnosis is borne out by the results of the DSM-5 field trial study reported by Joel E Dimsdale, MD, chair of the Somatic symptom disorder Work Group, at the 2012 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
15% of the ‘diagnosed illness’ study group, comprising patients with cancer or coronary disease, were caught by SSD and would meet the criteria for application of an additional mental disorder diagnosis.
26% of the ‘functional somatic’ study group, comprising patients with irritable bowel syndrome or chronic widespread pain, met the SSD criteria.
SSD has a high false positive rate – capturing 7% of the ‘healthy’ field trial control group.
It is disturbing that the SSD Work Group (which had included no primary care physicians or pediatricians) appears not to have undertaken any field trials into the safety of application of the SSD criteria in children and adolescents.
NCHS/CMS provides no references for data for the application of SSD in children within the Diagnosis Agenda, although the DSM-5 text clearly indicates APA’s intention that SSD is a diagnosis that may also be applied to children with persistent, distressing somatic symptoms.
+++
Potential implications for the application of a diagnosis of SSD:
I am not persuaded that the new SSD diagnosis can be safely applied outside the optimal conditions of field trials, in settings where practitioners may not necessarily have adequate time for, or instruction in administration of diagnostic assessment tools, and where decisions to code or not to code may hang on the arbitrary and subjective perceptions of a wide range of end-users who may lack clinical training in the application of mental disorder criteria.
Misapplication of highly subjective and loose, easily met criteria, especially in busy primary care practice, may result in inappropriate diagnoses of mental disorder and inappropriate medical decision making, with considerable implications for patients [11].
A recent study (Plouvier et al, 2014) found more frequent presentation with functional somatic symptoms and multiple prodromal symptoms in the two year period prior to diagnosis with Parkinson’s disease than controls [12].
Incautious application or a pre-existing diagnosis of SSD in the patient’s notes may blunt clinician alertness and receptivity to emerging prodromal symptomotology of serious disease.
Patients with chronic, multiple bodily symptoms due to rare diseases, difficult to diagnose conditions, or multi system diseases like Behçet’s disease, for which it can take several years to arrive at a diagnosis, may be especially vulnerable to missed diagnosis or to misdiagnosis with a mental disorder, impeding access to testing, investigations, timely diagnosis and early intervention (and may result in increased claims against practitioners for medical negligence).
With the elimination of the requirement that symptoms be “medically unexplained” and inclusion of the presence of a co-occurring physical health condition, a mental disorder diagnosis of SSD can be applied as a “bolt-on” to any chronic medical diagnosis: to patients with diabetes, angina, cancer, MS, cardiovascular disease, ME and CFS, IBS, chronic widespread pain (aka fibromyalgia), chronic pain conditions or persistent symptoms of unclear etiology.
Patients with Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), “almost a poster child for medically unexplained symptoms as a diagnosis,” according to the SSD Work Group chair, or with chronic Lyme disease, Gulf War illness, chemical injury and chemical sensitivity; women with potential symptoms of gynecological disease, like ovarian cancer – already often late-diagnosed because persistent symptoms had been initially dismissed as IBS or a menopausal-related bladder complaint; or women with endometriosis or interstitial cystitis may be particularly vulnerable to misapplication or misdiagnosis with a mental health disorder under SSD criteria.
(There is also a Brief somatic symptom disorder in DSM-5, cross-walked to ICD-9 F45.8, that can be applied where duration of symptoms is less than 6 months. Just one somatic symptom and one “disproportionate” psychobehavioral response to that symptom, for less than 6 months chronicity, now ticks the box for a mental health diagnosis.)
There has been considerable opposition to the introduction of this new, poorly tested construct into the DSM-5 amongst patients, carers, advocates, consumer organizations, mental health practitioners and clinicians and considerable concern for the implications for diverse patient populations that the Somatic Symptom Disorder category will provide a “dustbin diagnosis” for the so-called “functional somatic syndromes,” for those living with chronic pain and for patients with persistent, but as yet undiagnosed, symptoms of disease.
• NCHS/CMS has published no independent field trial data and provided no rationales or clinical and literature references to inform public responses.
Given the lack of published evidence for the validity and safety of SSD, there is insufficient basis for the approval of SSD for inclusion within ICD-10-CM and it would be scientifically unsafe, premature and against the public interest to include this new diagnostic construct within ICD.
The proposal for the addition of Somatic symptom disorder to the ICD-10-CM as an inclusion term to the Index and Tabular List should be rejected. There should be no implementation in October 2016 as an inclusion term to F45.1, or to any other existing code, or with a unique code created.
+++
Appendix:
Incautious, inept application of criteria resulting in a “bolt-on” psychiatric diagnosis of Somatic symptom disorder has far-reaching implications for diverse patient populations:
• Application of highly subjective and difficult to measure criteria could potentially result in misdiagnosis with a mental disorder, misapplication of an additional diagnosis of a mental disorder or missed diagnoses through dismissal and failure to investigate new or worsening somatic symptoms.
• Patients with cancer and life threatening diseases may be reluctant to report new symptoms that might be early indicators of recurrence, metastasis or secondary disease for fear of attracting a diagnosis of SSD or being labelled as “catastrophizers.”
• Application of an additional diagnosis of SSD may have implications for the types of medical investigations, tests and interventions that clinicians are prepared to consider and for which insurers are prepared to fund.
• Application of an additional diagnosis of SSD may impact payment of employment, medical and disability insurance and the length of time for which insurers are prepared to pay out.
• An SSD diagnosis may negatively influence the perceptions of agencies involved with assessment and provision of social care packages, disability adaptations, workplace accommodations, provision of education arrangements tailored to the needs of children with chronic illness, and the perceptions of medical staff during hospital and accident and emergency admission, and prejudice future employment options.
• Patients prescribed psychotropic drugs for perceived unreasonable levels of “illness worry” or “excessive preoccupation with symptoms” may be placed at risk of iatrogenic disease or subjected to inappropriate and costly behavioural therapies.
• Multi-system diseases like Multiple Sclerosis, Behçet’s disease or Systemic lupus can take several years before a diagnosis is arrived at. In the meantime, patients with chronic, multiple somatic symptoms who are still waiting for a diagnosis would be vulnerable to being labelled with a mental disorder.
• The burden of the DSM-5 changes to Somatoform disorders will fall particularly heavily upon women who are more likely to be casually dismissed when presenting with physical symptoms and more likely to be prescribed inappropriate antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications for them.
• Somatic symptom disorder allows for the application of a diagnosis of SSD in children and where a parent is perceived as being excessively concerned about a child’s symptoms.
The diagnostic term “Somatic Symptom Disorder” is already being applied to children despite the lack of a body of evidence for the reliability, safety and validity of the DSM-5 SSD criteria [13].
I am deeply concerned that NCHS/CMS is considering inclusion of a new diagnostic term within ICD when no studies have been carried out into the safety of its application in children and adolescents.
Families caring for children and young people with any chronic disease or condition may be placed at increased risk of wrongful accusation of “over-involvement” with their child’s symptomatology.
Where a parent is perceived as responsible for, or encouraging maintenance of “sick role behavior” or “secondary gains” in a child, this can trigger social services investigation, or court intervention for the forced removal of a sick child out of the home environment and into foster care or in-patient rehabilitation, or placement of the child on the “at risk register.”
This is already happening to families in the U.S., UK and Europe with a child or young adult with chronic illness, notably with Chronic fatigue syndrome or ME. It may happen more frequently with a diagnosis of SSD or of chronic childhood illness + SSD.
Where there are disputes between the family and clinicians over an assigned diagnosis or where there is disagreement between clinicians over the etiology of a child’s symptoms, an earlier or concurrent diagnosis of SSD may prejudice the family’s rights and the rights of the child or young person to determine what treatments are administered, where and by whom; or may be used to override or attempt to override the right to consent to treatments, or as a means of limiting parental access to the child and parental involvement in a treatment plan.
A diagnosis of SSD may also impact on a child’s access to suitable educational arrangements, including part-time school attendance, rest periods, reduced curriculum, home tutoring, examination concessions, provision of an amanuensis etc. and access to disability aids and adaptations, or to unhindered use of existing aids, such as wheelchairs.
Again, there is insufficient basis for the approval of SSD for inclusion within ICD-10-CM for application in children or adults. It is scientifically unsafe, premature and against the public interest to include this poorly tested diagnostic construct within ICD.
Thank you for your consideration.
+++
References:
1.Diagnosis Agenda,September 18-19, 2013 meeting of the ICD-9-CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee.
2.Summary of Diagnosis Presentations, September 18-19, 2013 meeting of the ICD-9-CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee.
3. DSM-5 Somatic Symptom Disorders Work Group Disorder Descriptions and Justification of Criteria – Somatic Symptoms, published May 2011, for second DSM-5 stakeholder review.
4. Robert L. Woolfolk and Lesley A. Allen (2012). Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Somatoform Disorders, Standard and Innovative Strategies in Cognitive Behavior Therapy, Dr. Irismar Reis De Oliveira (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0312-7
5. Ghanizadeh A, Firoozabadi A. A review of somatoform disorders in DSM-IV and somatic symptom disorders in proposed DSM-V. Psychiatr Danub. 2012 Dec;24(4):353-8.
6. Dimsdale JE, Creed F, Escobar J, Sharpe M, Wulsin L, Barsky A, Lee S, Irwin MR, Levenson J. Somatic Symptom Disorder: An important change in DSM. J Psychosom Res. 2013 Sep;75(3):223-8. Epub 2013 Jul 25.
7. Frances A. The new somatic symptom disorder in DSM-5 risks mislabeling many people as mentally ill. BMJ. 2013 Mar 18;346:f1580. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f1580.
8. Frances A. DSM-5 Somatic Symptom Disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2013 Jun;201(6):530-1. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0b013e318294827c.
9. Frances A, Chapman S. DSM-5 somatic symptom disorder mislabels medical illness as mental disorder. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2013 May;47(5):483-4. doi:10.1177/0004867413484525.
10. Wolfe F, Walitt BT, Katz RS, Häuser W. Symptoms, the nature of fibromyalgia, and diagnostic and statistical manual 5 (DSM-5) defined mental illness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia. PLoS One. 2014 Feb 14;9(2):e88740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088740. eCollection 2014.
11. Dimsdale JE. Medically unexplained symptoms: a treacherous foundation for somatoform disorders? Psychiatr Clin North Am 2011;34:511-3.
12. Plouvier AO, Hameleers RJ, van den Heuvel EA, Bor HH, Olde Hartman TC, Bloem BR, van Weel C, Lagro-Janssen AL2. Prodromal symptoms and early detection of Parkinson’s disease in general practice: a nested case-control study. Fam Pract. 2014 May 28. pii: cmu025. [Epub ahead of print]
13. Commonwealth of Massachusetts Juvenile Court Department, Court document, Honourable Joseph Johnston, March 25, 2014, Re: Care and Protection of Justina Pelletier: http://cbsboston.files.wordpress.com/2014/03/scan.pdf
Interest:
Carer/advocate for adult with long-term medical condition. Owner of website Dx Revision Watch, Monitoring the revision of DSM-5 and ICD-11. Co-author, journal papers and commentaries on the SSD construct (with Professor Allen Frances).