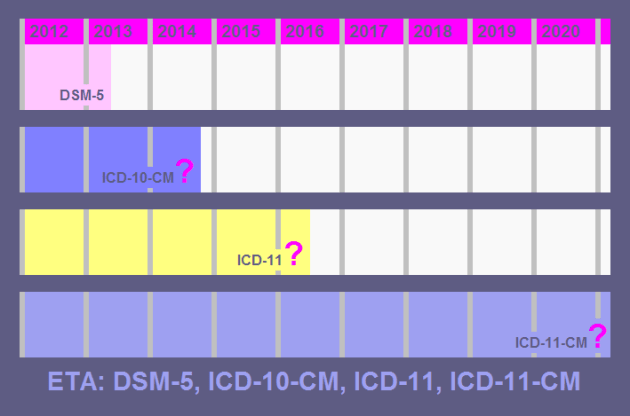
August 1, 2012
by meagenda
Round up: ICD- 11 PHC; ICD-11 Classification of Mood and Anxiety Disorders; Monograph: Public Health Aspects of Diagnosis and Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders; ASHA DSM-5 comments
1] Paper: The primary health care version of ICD-11: the detection of common mental disorders in general medical settings By David P. Goldberg, James J. Prisciandaro, Paul Williams
2] The ICD-11 Classification of Mood and Anxiety Disorders: background and options (Guest Editors: Mario Maj, Geoffrey M. Reed), World Psychiatry, Volume 11, Supplement 1, June 2012
3] Monograph: Public Health Aspects of Diagnosis and Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Refining the Research Agenda for DSM-5 and ICD-11 By Shekhar Saxena, Patricia Esparza, Darrel A. Regier, Norman Sartorius
4] Submissions to DSM-5 public reviews for drafts one, two and three by The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association
Post #195 Shortlink: http://wp.me/pKrrB-2pa
This post relates to the World Health Organization’s ICD-11 and ICD-11 PHC (Primary Care version), both currently under development. It does not apply to the existing ICD-10, ICD-10 PHC or to the forthcoming US specific “clinical modification” of ICD-10, known as ICD-10-CM.
Note on ICD-10 PHC and ICD-11 PHC
ICD-10 PHC (sometimes written as ICD-10-PHC or ICD10-PHC or ICD-10 PC), is a simplified version of the WHO’s ICD-10 chapter for mental and behavioural disorders for use in general practice and primary health care settings. This system has rough but not exact equivalence to mental disorders in the core ICD-10 classification.
The ICD-10 PHC describes 25 disorders commonly managed within primary care as opposed to circa 450 classified within Chapter V of ICD-10.
A chart showing the grouping of categories adapted from the full ICD-10 version for the existing ICD-10 PHC categories can be found here.
The revision of ICD-10 PHC, ICD-11 PHC, is currently under development.
Professor, Sir David Goldberg, M.D., Emeritus Professor, Institute of Psychiatry, King’s College, London, is a member of the DSM-5 Mood Disorders Work Group. Prof Goldberg also chairs the Consultation Group for Classification in Primary Care that is making recommendations for the 28 mental and behavioural disorders proposed for inclusion in ICD-11 PHC.
The majority of patients with mental health problems are diagnosed and managed by general practitioners in primary care – not by psychiatrists and mental health specialists. ICD10-PHC is used in developed and developing countries in general medical settings and also used in the training of medical officers, nurses and multi purpose health workers.
Further information on ICD-10 PHC and the development of the mental health disorders section of ICD-11 PHC can be found in these two documents:
1] Goldberg, D. Guest editorial. A revised mental health classification for use in general medical settings: the ICD11–PHC 1. International Psychiatry, Page 1, February 2011.
http://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/pdf/IPv8n1.pdf
2] 21st Century Global Mental Health by Dr Eliot Sorel, Professor, George Washington University, Washington D.C.
Publication date: August, 2012: http://www.jblearning.com/catalog/9781449627874/
Page 51, Sample Chapter 2: http://samples.jbpub.com/9781449627874/Chapter2.pdf
ICD Revision publishes the names and bios of members of the ICD-11 Revision Steering Group, ICD-11 Topic Advisory Groups, and International Advisory Group for the Revision of ICD-10 Mental and Behavioural Disorders.
But membership of the various sub working groups to the Topic Advisory Groups (TAGs), the names of external peer reviewers recruited by TAG Managing Editors for reviewing proposals and content and the membership of the advisory/consultation groups for the revision of the ICD Primary Care version have not been published by ICD-11 Revision.
The Abstract below lists members of the (WHO) Primary Care Consultation Group for the Revision of ICD-10 Mental and Behavioural Disorders.
1] Paper: The primary health care version of ICD-11: the detection of common mental disorders in general medical settings
http://www.ghpjournal.com/article/S0163-8343(12)00197-1/abstract
The primary health care version of ICD-11: the detection of common mental disorders in general medical settings
26 July 2012
David P. Goldberg, James J. Prisciandaro, Paul Williams
David P. Goldberg
Affiliations Primary Care Consultation Group, World Health Organization; and Institute of Psychiatry, KCL, London, UK
James J. Prisciandaro
Affiliations Department of Psychiatry, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston SC, USA
Corresponding author.
Paul Williams
Affiliations Health Services & Population Research, Institute of Psychiatry, KCL, London, UK
Received 31 January 2012; accepted 19 June 2012. published online 26 July 2012.
Corrected Proof
Abstract
Background
The primary health care version of the ICD-11 is currently being revised.
Aim
To test two brief sets of symptoms for depression and anxiety in primary care settings, and validate them against diagnoses of major depression and current generalised anxiety made by the CIDI.
Method
The study took place in general medical or primary care clinics in 14 different countries, using the Composite International Diagnostic Interview adapted for primary care (CIDI-PC) in 5,438 patients. The latent structure of common symptoms was explored, and two symptom scales were derived from item response theory (IRT), these were then investigated against research diagnoses.
Results
Correlations between dimensions of anxious, depressive and somatic symptoms were found to be high. For major depression the 5 item depression scale has marked superiority over the usual 2 item scales used by both the ICD and DSM systems, and for anxiety there is some superiority. If the questions are used with patients that the clinician suspects may have a psychological disorder, the positive predictive value of the scale is between 78 and 90%.
Conclusion
The two scales allow clinicians to make diagnostic assessments of depression and anxiety with a high positive predictive value, provided they use them only when they suspect that a psychological disorder is present.
This article is partly based on the work of the World Health Organization (WHO) Primary Care Consultation Group for the Revision of ICD-10 Mental and Behavioural Disorders, of which the first author is Chair. Other members of the group include Michael Klinkman (GP, United States; Vice Chairman); Sally Chan (nurse, Singapore), Tony Dowell (GP, New Zealand) Sandra Fortes (psychiatrist, Brazil), Linda Gask (psychiatrist, UK), KS Jacob (psychiatrist, India), Tai-Pong Lam (GP, Hong Kong), Joseph Mbatia (psychiatrist, Tanzania), Fareed Minhas (psychiatrist, Pakistan), Marianne Rosendal (GP, Denmark), assisted by WHO Secretariat Geoffrey Reed and Shekhar Saxena. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and, except as specifically noted, are not intended to represent the official policies and positions of the Primary Care Consultation Group or of the WHO.
Competing interests: David Goldberg is a consultant for Ultrasis and advises the World Health Organization and the American Psychiatric Association.
James Prisciandaro and Paul Williams have no competing interests
PII: S0163-8343(12)00197-1
doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2012.06.006
+++
2] The ICD-11 Classification of Mood and Anxiety Disorders: background and options (Guest Editors: Mario Maj, Geoffrey M. Reed), World Psychiatry, Volume 11, Supplement 1, June 2012
The PDF of this publication is free.
Note regarding references within these commentaries to DSM-5 proposals: Some of these commentaries were written prior to the release of the third DSM-5 draft for public review, in May 2012, and quote draft proposals as they had stood for the second draft.
For example, the commentary Hypochondriasis in ICD-11 by D.J. Stein, on Page 100, sets out in narrative form the DSM-5 Somatic Symptom Disorder Work Group proposals and criteria for Complex Somatic Symptom Disorder as they had stood in May 2011 and are not the most recent iteration.
DSM-5 proposals have not been finalized. Proposals as they stood in May 2012 for the third and final public review may be subject to further change before DSM-5 is published in May 2013. Please refer to the DSM-5 Development website for the most recent proposals and criteria sets for the categories and proposed categories that are discussed in these commentaries.
http://www.wpanet.org/uploads/WPA-WHO_Collaborative_Activities/WP_ICD-11%20Supplement.pdf
July 2012
The ICD-11 Classification of Mood and Anxiety Disorders: background and options (Guest Editors: Mario Maj, Geoffrey M. Reed) World Psychiatry, Volume 11, Supplement 1, June 2012
Contents
The development of the ICD-11 classification of mood and anxiety disorders
M. Maj, G.M. Reed Page 3
How global epidemiological evidence can inform the revision of ICD-10 classification of depression and anxiety disorders
L.H. Andrade, Y.-P. Wang Page 6
Specifiers as aids to treatment selection and clinical management in the ICD classification of mood disorders
D.J. Miklowitz, M.B. First Page 11
Challenges in the implementation of diagnostic specifiers for mood disorders in ICD-11
M.B. First Page 17
Cultural issues in the classification and diagnosis of mood and anxiety disorders
S. Chakrabarti, C. Berlanga, F. Njenga Page 26
Bipolar disorders in ICD-11
S.M. Strakowski Page 31
Changes needed in the classification of depressive disorders: options for ICD-11
E. Paykel, L.H. Andrade, F. Njenga, M.R. Phillips Page 37
Differentiating depression from ordinary sadness: contextual, qualitative and pragmatic approaches
M. Maj Page 43
Severity of depressive disorders: considerations for ICD-11
J.L. Ayuso-Mateos, P. Lopez-García Page 48
Dysthymia and cyclothymia in ICD-11
M.R. Phillips Page 53
Psychotic and catatonic presentations in bipolar and depressive disorders
S. Chakrabarti Page 59
Mixed states and rapid cycling: conceptual issues and options for ICD-11
M. Maj Page 65
How should melancholia be incorporated in ICD-11?
D. Moussaoui, M. Agoub, A. Khoubila Page 69
Postpartum depression and premenstrual dysphoric disorder: options for ICD-11
M.L. Figueira, V. Videira Dias Page 73
Disruptive mood dysregulation with dysphoria disorder: a proposal for ICD-11
E. Leibenluft, R. Uher, M. Rutter Page 77
Generalized anxiety disorder in ICD-11
M.K. Shear Page 82
Agoraphobia and panic disorder: options for ICD-11
D.J. Stein Page 89
Specific and social phobias in ICD-11
P.M.G. Emmelkamp Page 94
Hypochondriasis in ICD-11
D.J. Stein Page 100
+++
3] Public Health Aspects of Diagnosis and Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Refining the Research Agenda for DSM-5 and ICD-11
Note: Substantial extracts from this DSM-5 and ICD-11 monograph can be previewed online on the Amazon site via the “LOOKINSIDE!” function. Greater access to preview content is available to Amazon account holders. Extracts can also be previewed via Google:
Preview via Amazon “LOOKINSIDE!”:
http://www.amazon.com/Aspects-Diagnosis-Classification-Behavioral-Disorders/dp/0890423490#reader_0890423490
Preview via Google Books:
http://tinyurl.com/DSM5-ICD11-Monograph
Public Health Aspects of Diagnosis and Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Refining the Research Agenda for Dsm-5 and ICD-11
By Shekhar Saxena, Patricia Esparza, Darrel A. Regier, Norman Sartorius
(c) 2012
Paperback: 303 pages
Publisher: American Psychiatric Publishing; 1 edition (April 30, 2012)
Public Health Aspects of Diagnosis and Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Refining the Research Agenda for DSM-5 and ICD-11
[Paperback]
Shekhar Saxena (Author), Patricia Esparza (Author), Darrel A. Regier (Author), Benedetto Saraceno (Author), Norman Sartorius (Author)
Shekhar Saxena, M.D.,is Director of the Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse at the World Health Organization in Geneva, Switzerland.
Patricia Esparza, Ph.D.,is Research Professor and clinical psychologist in the Department of Psychology and Counseling at Webster University in Geneva, Switzerland.
Darrel A. Regier, M.D., M.P.H.,is Director of the American Psychiatric Institute for Research and Education and Director of the Division of Research at the American Psychiatric Association in Arlington, Virginia; and Vice-Chair of the DSM-5 Task Force.
Benedetto Saraceno, M.D.,FRCPsych,is Professor of Psychiatry and Director of the World Health Organization Collaborating Center on Mental Health of the University of Geneva in Geneva, Switzerland.
Norman Sartorius, M.D., Ph.D.,is President of the Association for the Improvement of Mental Health Programs in Geneva, Switzerland.
Book Description
Publication Date: April 30, 2012 | ISBN-10: 0890423490 | ISBN-13:
978-0890423493 | Edition: 1
“Public Health Aspects of Diagnosis and Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders: Refining the Research Agenda for DSM-5 and ICD-11” provides a comprehensive summary of the current state of mental health classification in the United States and internationally, fostering a better understanding of primary research and clinical needs and facilitating the efforts of service planners, researchers and trainees to address current use of psychiatric diagnosis in the public health sector. The volume reflects the proceedings of a research planning conference convened by the APA and World Health Organization (WHO) that focused on public health aspects of the diagnosis and classification of mental disorders. Highly relevant to the ongoing development of DSM-5 and ICD-11, the book includes the background papers prepared and presented by the Conference Expert Groups. The resulting collection: – Discusses the current state of mental illness prevention efforts and the role of public health in supporting them–critical topics, given that development of effective strategies to reduce mental illness around the world depends on the accuracy with which risk and protective factors can be identified, defined, and understood. – Features international perspectives on public health implications of psychiatric diagnosis, classification, and service, providing viewpoints that are broad and more globally relevant. – Views mental health education, and awareness on a macro level, including its impact on social and economic policy, forensics and the legal system, and education. This approach facilitates the continued development of a research base in community health and promotes the establishment of programs for monitoring, treating, and preventing mental illness. – Addresses many fascinating and clinically relevant issues, such as those raised by the concept and the definition of mental disorders and how these impact psychiatric services and practice by individual providers.
This collection should prove useful to the advisory groups, task forces, and working groups for the revision of these two classifications, as well as for researchers in the area of diagnosis and classification, and more generally in public health.
+++
4] Submissions to DSM-5 public reviews for drafts one, two and three by The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)
The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) represents people with speech, language, and hearing disorders and advocates for services to help them communicate effectively.
ASHA submitted comments during all three DSM-5 draft comment periods:
ASHA submission April 2010 [PDF]; June 2011 [PDF]; June 2012 [PDF]
ASHA Letter sent June 2012 [PDF]
DSM-V Revisions To Move Forward (ASHA Leader article)
all documents available from this page:
http://www.asha.org/SLP/DSM-5/
+++
Key ICD-11 links and documents
ICD-11 Beta drafting platform | Publicly viewable version
WHO ICD Revision | Main WHO website: Revision Steering Group and Topic Advisory Groups
ICD-11 Revision site | Revision resources [Google site currently unavailable]
ICD-11 Revision site Documents Page | Key revision documents and meeting materials [Google site currently unavailable]
ICD-11 Revision Information |
ICD-11 Timeline |
ICD Information Sheet |
Revision News |
Steering Group |
Topic Advisory Groups |
ICD-11 YouTube Channel | Video reports
ICD-11 on Facebook |
ICD-11 on Twitter |
ICD-11 Blog | Not updated since October 2009
ICD-11 YouTubes collated on Dx Revision Watch ICD-11 YouTubes |
WHO Publications
ICD-10 Tabular List online Version: 2010 | International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision Version: 2010, Tabular List of inclusions and Chapter List
ICD-10 Volume 2: Instruction Manual | Volume 2 online Version: 2010 PDF Download
ICD-10 for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Diagnostic Criteria for Research | PDF download
ICD-10 for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines | PDF download
ICD-10 Volume 3: The Alphabetical Index | WHO does not make ICD-10 Volume 3: The Alphabetical Index available online
About the World Health Organization (WHO)
The WHO Family of International Classifications
History of ICD