BDS, BDDs, BSS, BDD unscrambled
June 19, 2013
Post #268 Shortlink: http://wp.me/pKrrB-3fA
BDS, BDDs, BSS, BDD and ICD-11, unscrambled
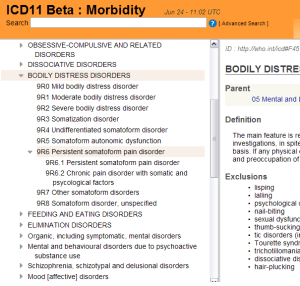
There are two WHO convened working groups charged with making recommendations for the revision of ICD-10’s Somatoform Disorders: the Primary Care Consultation Group (known as the PCCG) and the Expert Working Group on Somatic Distress and Dissociative Disorders (known as the S3DWG).
The revision of ICD-11 is being promoted as an open and transparent process. But to date, neither working group has published progress reports for stakeholder consumption and neither group has published its emerging proposals in public access journals.
Content populated in the public version of the ICD-11 Beta drafting platform sheds little light on proposals.
Consequently, there is considerable confusion around what is being recommended for the revision of ICD-10’s Somatoform Disorders, whether consensus between the two working groups has been reached, and what proposals will progress to field testing during the next two years.
ICD-11 Revision has been asked to clarify when it intends to define and characterize its current proposals within the Beta drafting platform.
The notes below set out some of what is known about the two working groups’ emerging proposals, how they diverge and how they compare with DSM-5’s Somatic Symptom Disorder and with Fink et al’s Bodily Distress Syndrome.
Caveat: the proposals of the two ICD-11 working groups may have undergone revision and refinement since emerging proposals were published, in July and December, last year; the two groups may or may not have reached consensus over how this proposed new ICD construct should be defined and characterized, its inclusions, exclusions and differential diagnoses, or what name it should be given.
What is Bodily Distress Syndrome (BDS)?
Bodily Distress Syndrome is the name given to a disorder construct developed by Per Fink and colleagues, Aarhus University, that is already in use in Danish research studies and in clinical settings [1].
BDS is described by its authors as “a unifying diagnosis that encompasses a group of closely related conditions such as somatization disorder, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome.”
Per Fink and colleagues are lobbying for BDS to be integrated into forthcoming classification systems and adopted as a diagnosis by primary care practitioners.
Their proposal is for reclassifying somatoform disorders, pain disorder, neurasthenia and the so-called functional somatic syndromes, including fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome, under a new classification, Bodily Distress Syndrome.
They consider these should be treated and managed as subtypes of the same disorder with CBT, GET, “mindfulness therapy” and in some cases, antidepressants.
The PDF format slide presentation in reference [2] will give an overview of BDS and there is more information and links in an earlier post, in reference [3].
Is Fink et al’s Bodily Distress Syndrome construct the same as DSM-5’s SSD?
No, Bodily Distress Syndrome is a different construct to DSM-5’s Somatic Symptom Disorder.
Psychological or behavioural characteristics, central for the diagnosis of SSD, do not form part of the BDS criteria.
For BDS, physical symptoms are central to the diagnosis, which is based on identification of symptom patterns (not symptom count) from four body systems:
Cardiopulmonary/autonomic arousal; Gastrointestinal arousal; Musculoskeletal tension; General symptoms.
There is a “Modest” BDS (single-organ type) and a “Severe” BDS (multi-organ type).
If the symptoms are better explained by another disease, they cannot be labelled BDS.
The graphic below compares mutli-organ Bodily Distress Syndrome with Somatic Symptom Disorder, as the DSM-5 draft criteria had stood, in May 2012.
Note the defining characteristics of the DSM-5 SSD construct: the SSD definition calls for positive psychobehavioural characteristics (excessive or maladaptive responses or associated health concerns) in response to persistent distressing somatic symptoms; the requirement that the symptoms are “medically unexplained” is not central to the diagnosis and the symptoms may or may not be associated with a well-recognised medical condition.
The SSD diagnosis can be made in the presence of one or more unspecified, somatic symptoms associated with general medical conditions and diagnosed disease, like multiple sclerosis, cancer, diabetes or angina, or in the so-called “functional somatic syndromes” (for example, IBS, CFS or fibromyalgia) or in complaints with unclear etiology.
Compare Fink et al’s BDS with DSM-5’s SSD, in the table, below:
Depending on screen size/resolution, graphic may not display in full. Click on the image and the image file will load. Graphic: Suzy Chapman