WHO considers further extension to ICD-11 development timeline
September 15, 2013
Post #275 Shortlink: http://wp.me/pKrrB-3sc
Information in this report relates to the World Health Organization’s ICD-11, currently under development. It does not apply to the current ICD version (ICD-10) or to the forthcoming US specific “clinical modification” of ICD-10, known as ICD-10-CM.
Timeline slippage
Documents posted recently by the World Health Organization (WHO) indicate that ICD Revision is failing to meet development targets and a further extension to the ICD-11 timeline is under consideration.
ICD serves as the international health information standard for the collection, classification, processing and presentation of disease-related data in national and global health statistics.
The 10th edition (ICD-10) was adopted by the World Health Assembly in 1990.
The development process for the next edition (ICD-11) began in April 2007, with ICD-11 scheduled for dissemination by 2012 and the timelines for the development of ICD-11 and DSM-5 running more or less in parallel [1] [2].
Early on in the revision process, the ICD-11 dissemination date was extended. By 2009, the final draft was scheduled for World Health Assembly (WHA) approval in 2014. In order to be ready for global implementation in 2015, the technical work on ICD-11 would need to be completed by 2012 [3].
The WHA approval date was subsequently shunted from 2014 to 2015 – four years later than originally planned and the current, projected implementation date is 2016+.
“…And just a small detail: who will do all this work?” [4]
ICD-11 is a very ambitious and under-resourced project. Given the scale of the undertaking, the technical complexity, the limited funding and human resources, the feasibility of the project reaching its targets by May 2015 has proved unrealistic.
I have written a number of times on this site that I did not envisage dissemination of ICD-11 by 2016 without some scaling back of the project’s scope – or an announcement, at some point this year, of a further extension to the timeline.
ICD-11 Revision Steering Group considers its options
WHO has recently posted a meeting materials document [5] and a slide presentation [6] which summarize, inter alia, ICD-11’s progress, current development status and timelines for finalization date and approval by WHO Governing Bodies.
ICD Revision is considering extending the timeline by up to a couple of years.
This 14 page document Committee for the Coordination of Statistical Activities, Twenty-second Session 4-6 September 2013, Items for discussion and decision: Item 8 of the provisional agenda can be downloaded here
or opened on Dx Revision Watch: PDF: SA-2013-12-Add1-Health-WHO
It summarizes the status of the ICD Revision process under section headings:
1. Background: need and mandate
2. General organization structure of the multiple streams of work
3. Progress and current status
4. The remaining steps
5. Further maintenance of ICD after finalization
6. Timelines for the finalization date and approval by WHO Governing Bodies
Extracts from the document setting out the rationale and options for postponement of WHA Approval:
[…]
3. Progress and Current Status of ICD Revision:
[…]
BETA PHASE:
At this point in time, 1 September 2013, an ICD2013 Beta version has been produced for review purposes and field trials after 6 years of drafting phases.
The current ICD 2013 Beta version has relatively stable classification lists (i.e. linearizations) for Mortality and Morbidity recording. It will be reviewed by the specific Mortality Reference Group and the Morbidity Reference Group to see how well it fits the purpose and proposed transition from ICD‐10.
In addition, the Beta version has planned processes for:
(i) Systematic international scientific peer review
(ii) Submission of additional proposals from public groups and scientists
(iii) Conducting field trials for its applicability and reliability
(iv) Production support in multiple languages (translations) starting with WHO official languages
(v) Preparations for transitions from ICD‐10 to ICD‐11.[…]
6. Timelines
The current ICD Revision Process timeline foresees that the ICD is submitted to the WHA in 2015 May and could then be implemented. Between now and 2015, there remains 20 months to conduct the remaining tasks summarized above as: 1. Reviews, 2. Additional Proposals, 3. Field Trials, 4. Translations, and 5. Transition Preparations.
Given the technical requirements these steps could be expedited in the next 20 months. The experience obtained thus far, however, suggests that this timeframe will be extremely tight for paying due diligence to the work especially in terms of: appropriate consultations with expert groups; communication and dissemination with stakeholders; and sufficient time for field testing in multiple countries and settings, and carrying out the resulting edits.
WHO Secretariat would like to discuss this with all stakeholders and evaluate the possible options:
a. Keep ICD submission to WHA to 2015 as originally planned and implementation / adoption date may be free by any Member State (current position – no change).
b. Postpone submission to WHA to a later year to allow longer time for field trials and other transition preparations.
[…]
In conclusion:
(a) WHO Secretariat could produce an ICD 2015 ready including Mortality and Morbidity Linearizations, Reference Guide and Index with the appropriate resolution to go to the World Health Assembly. This timeframe, however, is extremely tight for paying due diligence to the work especially in terms of: appropriate consultations with expert groups; and sufficient time for field testing in multiple countries and settings, and carrying out the resulting edits
(b) If the timeline is advanced to 2016, there will be more time to have ICD 2016 version with more translations and incorporations of some field tests results.
(c) If the timeline is advanced to 2017, ICD 2017 will be ready with most Field Test results incorporated and maintenance scheme tested.
[…]
If WHO/ICD-11 Revision Steering Group does elect to postpone submission for WHA approval until May 2017, dissemination of ICD-11 may not be scheduled before 2018.
Once approved and released, adoption of ICD-11 won’t happen overnight. It may take several years before WHO Member States adopt ICD-11. Low resource and developing countries may also take longer to prepare for and transition to the new edition.
Note for US readers: According to Page 3332 of DHSS Office of Secretary Final Rule document (Federal Register / Vol. 74, No. 11 / Friday, January 16, 2009 / Rules and Regulations):
“…We [ICD-9-CM Coordination and Maintenance Committee] discussed waiting to adopt the ICD-11 code set in the August 22, 2008 proposed rule (73 FR 49805)…
“…However, work cannot begin on developing the necessary U.S. clinical modification to the ICD-11 diagnosis codes or the ICD-11 companion procedure codes until ICD-11 is officially released. Development and testing of a clinical modification to ICD-11 to make it usable in the United States will take an estimated additional 5 to 6 years. We estimated that the earliest projected date to begin rulemaking for implementation of a U.S. clinical modification of ICD-11 would be the year 2020.” [7]
This projection, in early 2009, would have been based on the assumption that ICD-11 was anticipated to be finalized and submitted for WHA Approval by 2014 (now potentially shifting to 2017).
An additional two year delay in the finalization of the ICD-11 code sets would likely impact on the development process for a clinical modification of ICD-11 for US specific use, kicking adaptation and implementation of an ICD-11-CM even further down the road.
This slide presentation, below, was uploaded to Slideshare on September 9 by Dr Bedirhan Üstün, Coordinator, Classification, Terminology and Standards, World Health Organization, and also sets out the postponement options now under consideration:
Slide presentation: World Health Organization Classifications, Terminologies, Standards
ICD Revision: Quality Safety Meeting 2013 September 9-10
Where are we? What remains to be done? Shall we have ICD WHA submission in 2015 or later?
http://www.slideshare.net/ustunb/icd-2013-qs-tag-26027668
Slide 29:
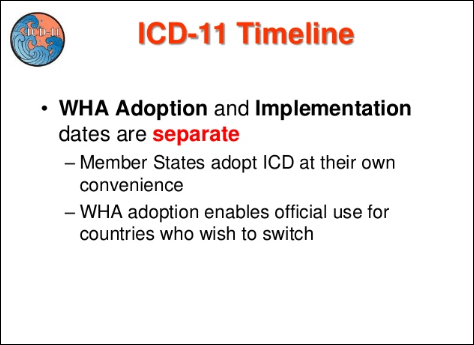
Slide 30:
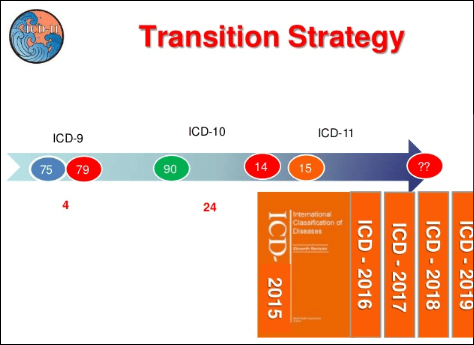
Slide 34:

Slide 35: [WHA Approval – options under consideration]

References
1. Agenda Item No. 25: Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) and Involvement of Psychology International Union of Psychological Science Committee on International Relations Action, March 28–30, 2008 IUPsyS Mar 08 Agenda Item 25 ICD-10
2. Letter Saxena, WHO, to Ritchie, IUPsyS (International Union for Psychological Science), August 2007 Exhibit 1 WHO Letter Aug 07
3. Dr Geoffrey Reed, Ph.D., May 2009, personal correspondence.
4. Closing remarks, PowerPoint presentation: “Proposal for the ICD Beta Platform”, Stanford team, 12.04.11, WHO, Geneva.
5. Committee for the Coordination of Statistical Activities, Twenty-second Session 4-6 September 2013, Items for discussion and decision: Item 8 of the provisional agenda, 3 September 2013 Full document in PDF format
6. Slide presentation: ICD Revision: Where are we? Bedirhan Ustun, World Health Organization Classifications, Terminologies, Standards, ICD Revision: Quality Safety Meeting 2013, September 9-10, 2013 http://www.slideshare.net/ustunb/icd-2013-qs-tag-26027668
7. DHSS Office of Secretary Final Rule document (Federal Register / Vol. 74, No. 11 / Friday, January 16, 2009 / Rules and Regulations), Page 3332.

 2013 All rights reserved. Current Biology,
2013 All rights reserved. Current Biology, 
